Quick Introduction To Podman
Many daemons run with root user privileges which can be a security vulnerability because of access to read any file, install programs and edit applications.
Podman allows a regular user to manager their pods (containers) without the need for root user privileges. Podman can be used as an alternative to Docker on Linux and other operating systems such as MacOS and Windows.
By default, Podman stores containers in your home folder. This could be an issue if the home folder is on a smaller drive or partition (common for smaller faster SSD Drives). It is possible to move the container storage to another location.
Podman was originally used to compile PHP for the Learning PHP eBook.
This tutorial will create a container that uses Fedora Linux and Apache Web Server to run a simple index.html
For this example, I will assume that Podman is installed on your platform of choice. A text document that contains all the commands a user could call to assemble an image is called a Dockerfile when using Docker. Podman can use any name for the reference and I will called it a Dockerfile so that Docker fans can follow along by replacing “podman” with “docker”.
Dockerfile
FROM fedora:latest RUN dnf -y update && dnf -y install httpd git && dnf clean all COPY index.html /var/www/html/index.html COPY index.html /var/www/html/index.html ENTRYPOINT /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
Build And Run
podman build --tag fedora:myhttpd -f ./Dockerfile podman run -p 8080:80 --name myhttpd --rm fedora:myhttpd
View
Open your web browser and point it to http:localhost:8080 and then wait for the HTML page to load.
Screenshots:
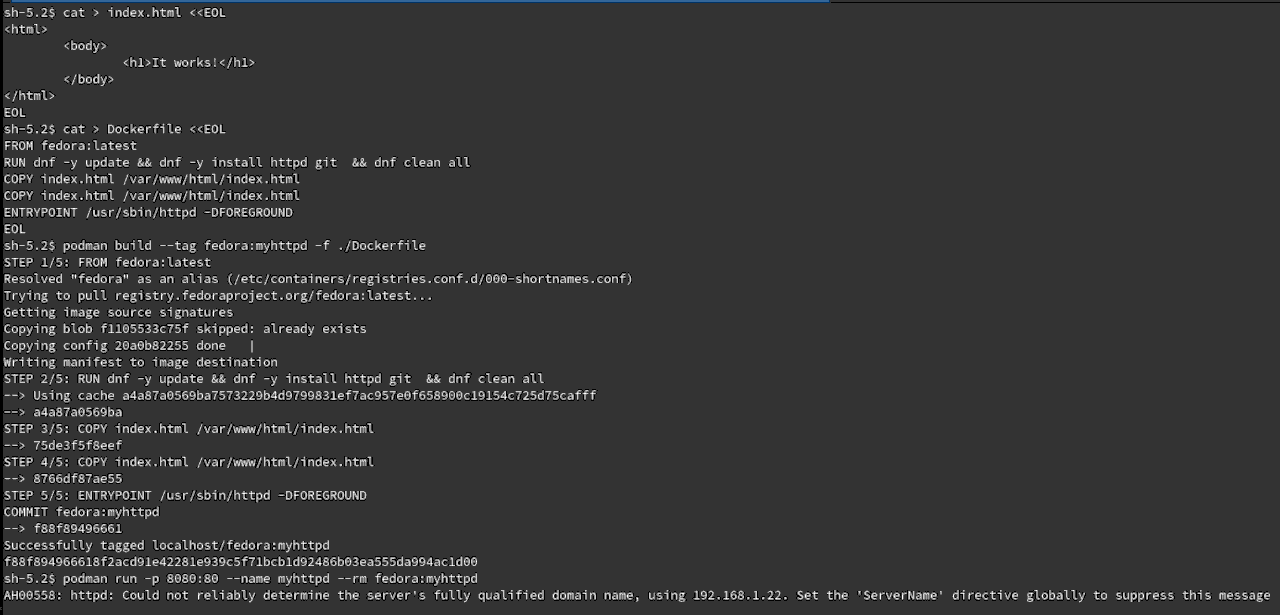
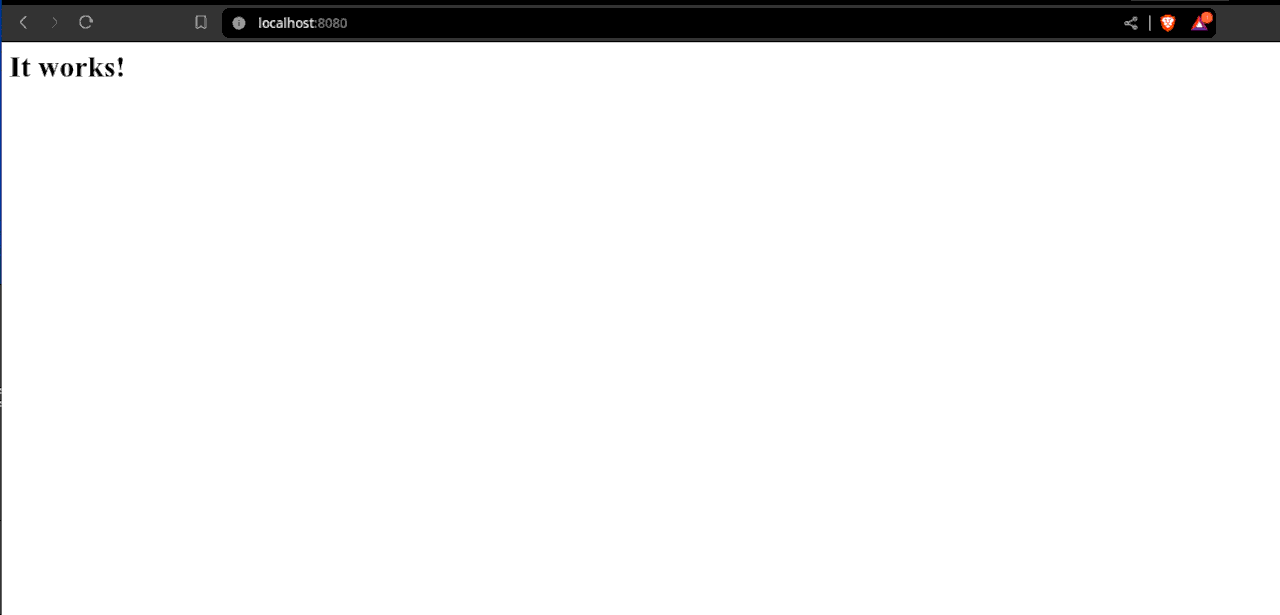
Conclusion:
In summary, Podman can be used a replacement for Docker. Podman uses the same commands as Docker and is daemonless, allowing a regular user to manage containers.