Mastering Git Difftool
The git diff is a command used to compare changes between 2 versions of a file or between 2 commits in a Git Repository. Git also allows a user to set their preferred diff tool using the git difftoolcommand.
Web designers and application developers can use Git to track changes or versions. Git is a distributed version control system (dvcs). Every repository (local copy of source code) contains the complete history therefore rendering a central server redundant or network independent.
The focus of this tutorial will be using the Git Difftool.
- Setting up a local repository and initializing your project.
- Making changes, staging files, and committing with meaningful messages.
- Pushing your changes to a remote repository.
Requirements For Using Git
Glossary:
Distributed Version Control System
(DVCS) tracks versions of files.
Software Collaboration
Teams working together on projects.
Repository
Project storage space where all changes to files are tracked.
Branch
Enables developers to work on different versions of the project.
Stage
Prepare for a commit by adding files to a staging area.
Commit
Captures staged changes as a snapshot to add to repository’s history.
Diff
Generate set of differences between 2 files or folders.
Patch
Apply a set of differences to update files.
Tools
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text editor | For creating and editing source code | Apache Netbeans IDE |
| SSH | Secure Shell Client | OpenSSH |
| Shell Access | Access to the command line. | Terminal |
| Git | Distributed version control system. | Git |
| Name | Description | Example |
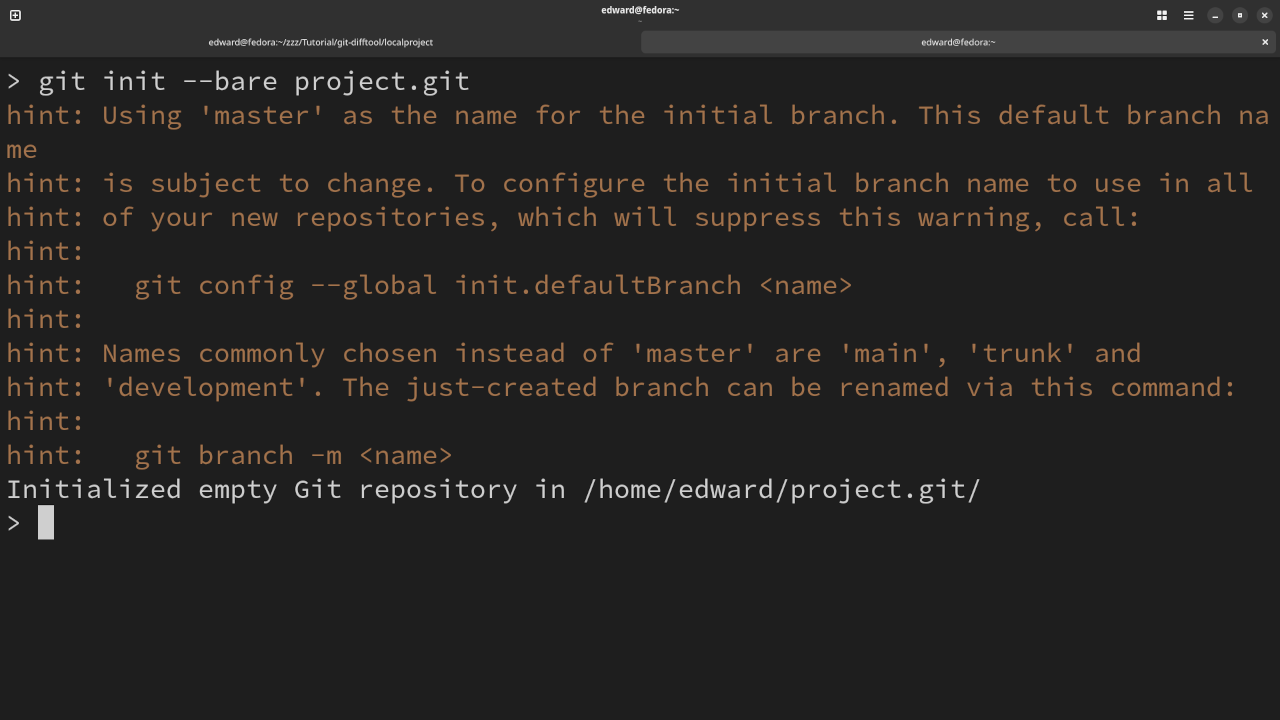
Create Remote Repository
# Create And Initialize Remote Repository # git init --bare project.git
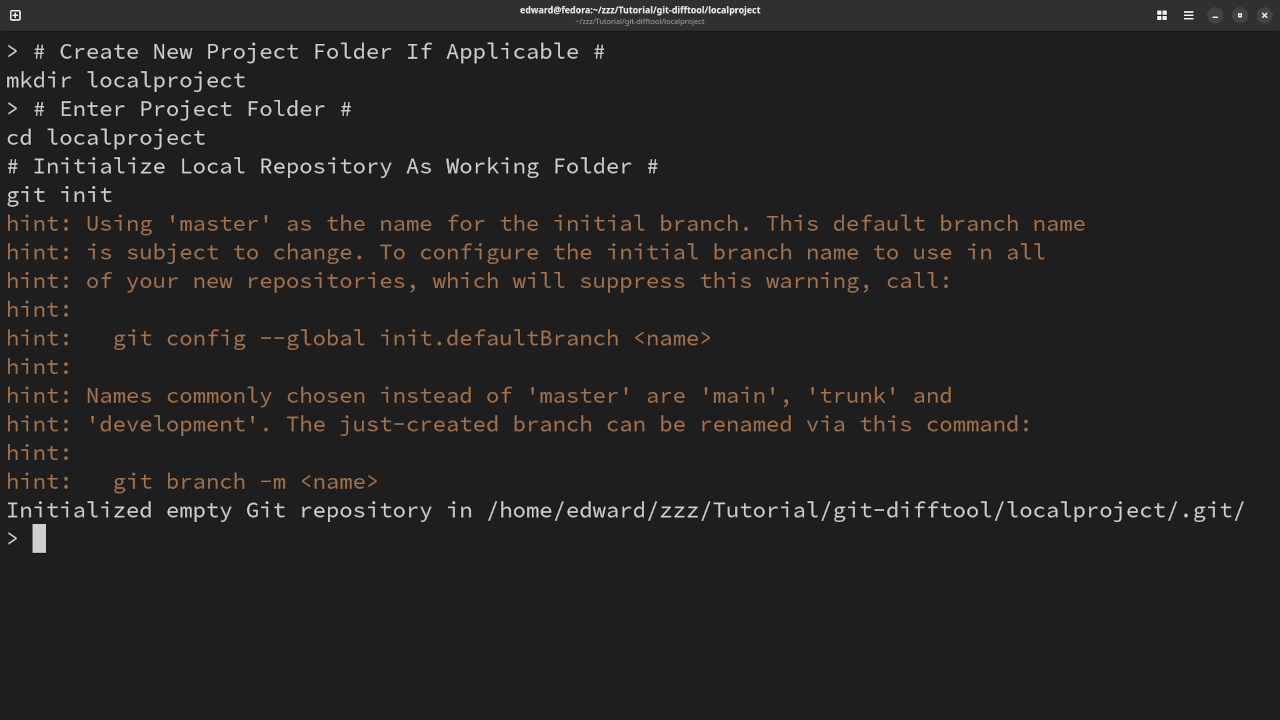
Create Local Repository
# Create New Project Folder If Applicable # mkdir localproject # Enter Project Folder # cd localproject # Initialize Local Repository As Working Folder # git init
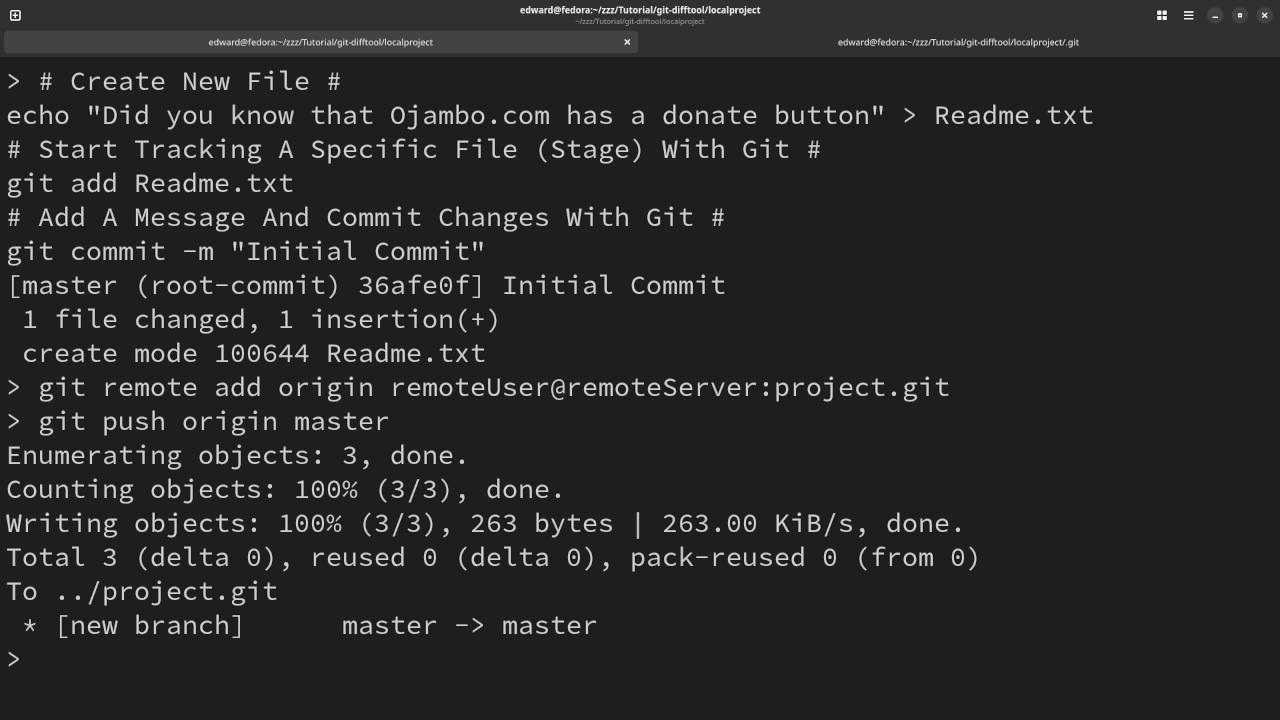
Add New File To Local Repository
# Create New File # echo "Did you know that Ojambo.com has a donate button" > Readme.txt # Start Tracking A Specific File (Stage) With Git # git add Readme.txt # Add A Message And Commit Changes With Git # git commit -m "Initial Commit"
Connect Local Project To Remote Repository
# Add Remote Repository In Local Project # git remote add origin remoteUser@remoteServer:project.git
Push Changes To Remote Repository
# Push Local Branch Changes To Remote Branch # git push origin master
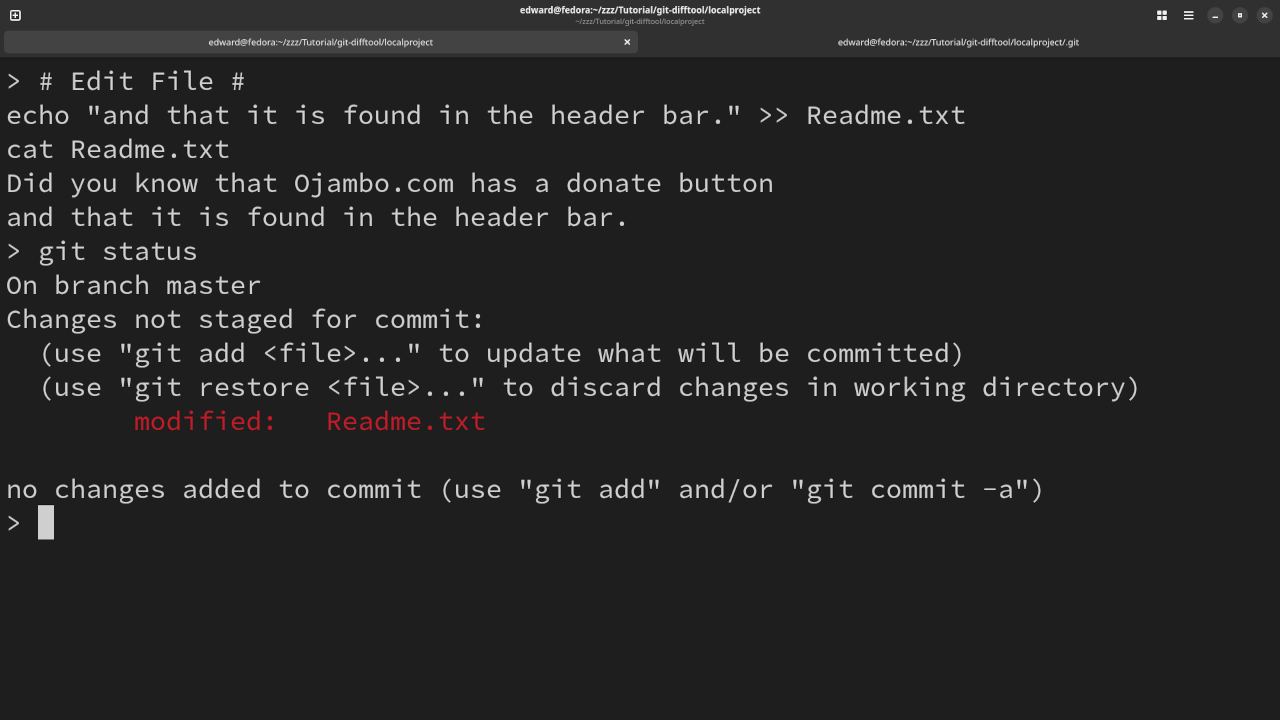
Modify Current File
# Edit File # echo "and that it is found in the header bar." >> Readme.txt cat Readme.txt # Check Status # git status
Compare Changes
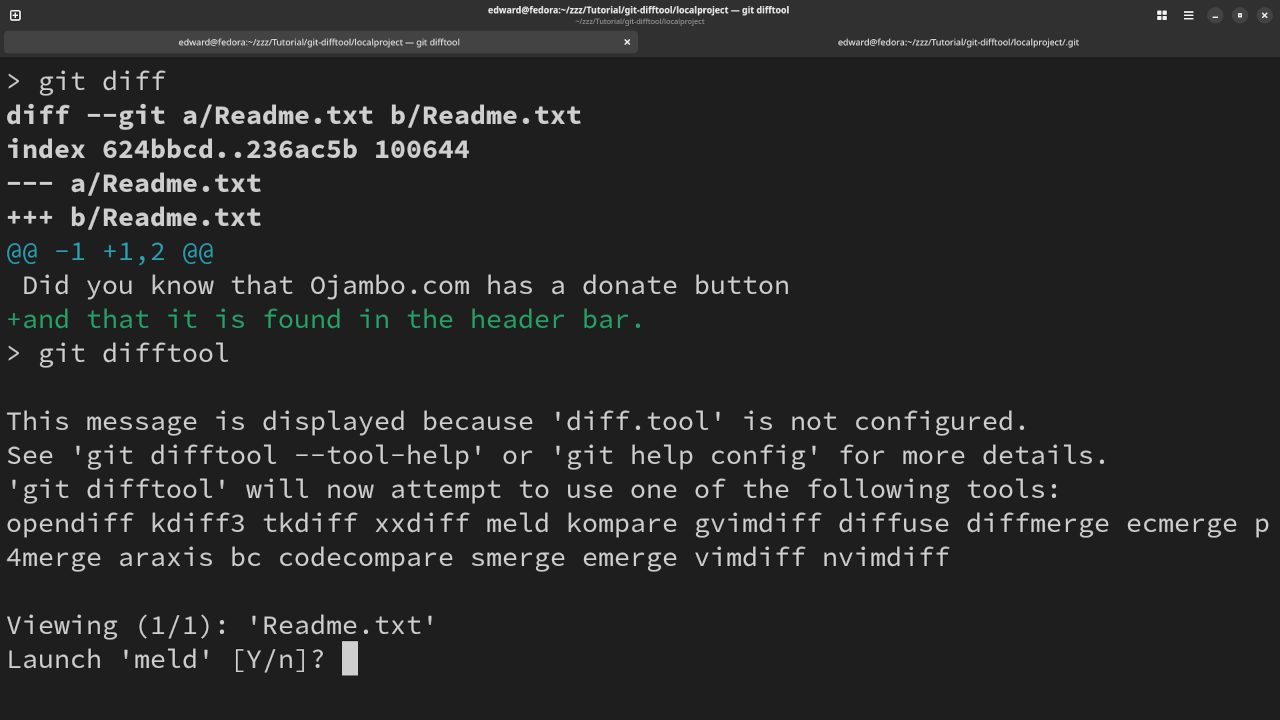
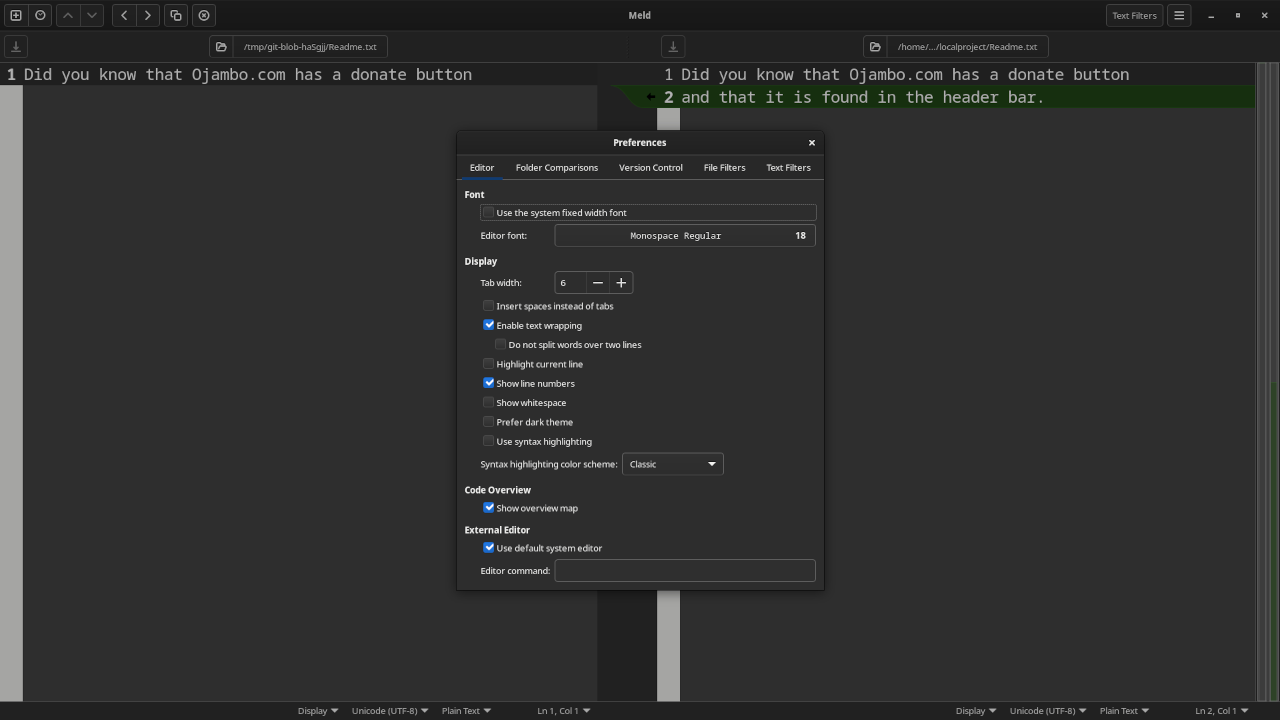
# Compare Changes Within Git Repository # git diff # Compare Changes Using External Diff Tool # git difftool
Optionally Set Default Diff Tool
# Modify Git Configuration To Set Meld As Diff Tool # git config --global diff.tool meld
Download And Install Git
Download
Git can be downloaded from Distributed Version Control System. Then the downloaded file is extracted directly on the server or locally before individual files are uploaded if applicable.
Diffutils can be downloaded from GNU Diffutils. Then the downloaded file is extracted directly on the server or locally before individual files are uploaded if applicable.
Meld can be downloaded from Visual Diff And Merge Tool. Then the downloaded file is extracted directly on the server or locally before individual files are uploaded if applicable.
Explanation:
- The remote repository is created with bare because a working folder is not needed or it might be elsewhere such as for websites.
- The add command stages the desired files.
- The commit command will record a snapshot.
- The status command displays the state of the working folder and staging area.
- During the initial push, 2 branches are created, locally it is master and remote is origin.
- The
git diffcommand is used to view changes made relative to the index (staging area for the next commit). - The
git difftoolcommand is used to temporary configure the diff tool Git uses. - The
git configcommand is used to permanently configure the diff tool Git uses.
The remote repository is normally hosted on a remote location and accessed through SSH or a platform-specific method. During the commit, a message that clearly explains the changes made and why they were made helps future developers understand the context.
Usage
You can use any IDE or text editor and the command-line or a web browser (if applicable) to run Git commands. For this tutorial, Git was used for source code management. Git is cross-platform compatible (Unix, Linux, MacOS and Windows). Diff was used on text files and is also cross-platform compatible. Meld was used on text files and is also cross-platform compatible.
Open Source
Git is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 2.0. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Diffutils is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 3.0 or later. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Meld is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 2.0 or later. The copyleft license comes with strict rules and requirements to ensure the software remains free and open-source. It allows commercial use, modification, distribution, and allows making derivatives proprietary, consult the license for more specific details.
Conclusion:
Git is a popular source code management system. Git is a distributed revision control system because every “working directory” contains the complete history and therefore revision tracking capabilities.
Git can work on remote servers or local machines to push committed changes and clone. The git difftool can can be used to choose your preferred diff tool.
If you enjoy this article, consider supporting me by purchasing one of my WordPress Ojambo.com Plugins or programming OjamboShop.com Online Courses or publications at Edward Ojambo Programming Books or become a donor here Ojambo.com Donate
References:
- Customer Sets Price Plugin for WooCommerce on Ojambo.com
- Learning JavaScript Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning Python Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning PHP Course on OjamboShop.com
- Learning JavaScript Paperback on Amazon
- Learning JavaScript Ebook on Amazon
- Learning Python Ebook on Amazon
- Learning PHP Ebook on Amazon
- OjamboServices.com For Custom Websites, Applications & Tutorials
Disclosure: Some of the links above are referral (affiliate) links. I may earn a commission if you purchase through them - at no extra cost to you.
